Biodiversity 1mn
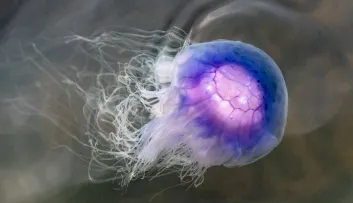
Jellyfish
Why do jellyfish sting?
A jellyfish is stinging, but what triggers the sting?

Jellyfish tentacles are made up of stinging cells (cnidocytes) that contain venom, enabling them to catch their prey and paralyse it before eating it.
It's a formidable predation technique!
When these cells come into contact with the skin of bathers or fish, they inject their venom through a tiny harpoon, causing itching.
This burning sensation is explained by the fact that the cnidocytes remain attached to the skin and continue to inject their venom.
What's more, even washed up on the sand, they can still inflict painful burns on anyone who gets too close. So don't touch them.